A 480 V three-phase system has two resistive loads with the following information:
- Balanced delta-connected load that draws 12 A in each phase
- Balanced wye-connected load
- A reading has been taken and the total line current is 47 A
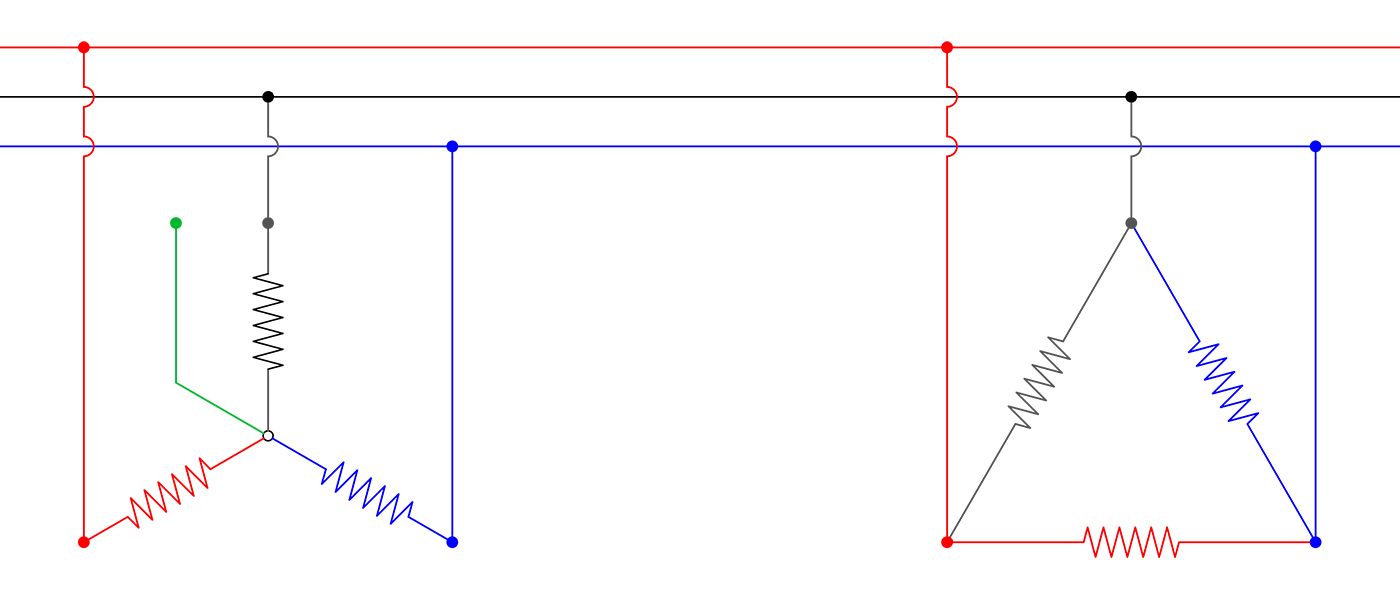
-
Since we already know that IPHASE = 12 A in the Delta, and VLINE = 480 V the first thing we should solve for is the impedance of the delta-connected laod (4).
In a Delta system VPHASE = VLINE and since Ohm's law states that R = V ÷ I we can calcualte the resistance of the delta-connected load.
RPHASE (DELTA) = 480 V ÷ 12 A
RPHASE (DELTA) = 40 Ω -
Next we can solve for the line current in the delta (1).
In a Delta system ILINE = IPHASE x 1.732 (Square Root of 3).
ILINE (DELTA) = 12 A x 1.732
ILINE (DELTA) = 20.785 A -
Now we can find the line current in the Wye-Connected load.
Since both loads are purely resistive, the current values are in phase with each other. This means we can simply take the total system line current (47 A) and subtract the Delta line current (20.785 A) to get the Wye Line current.
ILINE (WYE) = ILINE (TOTAL) - ILINE (DELTA)
ILINE (WYE) = 47 A - 20.785 A
ILINE (WYE) = 26.215 A -
Lastly, we can solve for the impedance of the Wye-Connected load.
To do this, we first need to calculate the Phase Voltage in the Wye. In a Wye system, VPHASE = VLINE ÷ 1.732 (Square Root of 3)
VPHASE (WYE) = 480 V ÷ 1.732
VPHASE (WYE) = 277.128In a Wye system, IPHASE = ILINE
We can now use Ohm's law to calculate for the resistance in each phase of the Wye system.
RPHASE (WYE) = VPHASE (WYE) ÷ IPHASE (WYE)
RPHASE (WYE) = 277.128 ÷ 26.215
RPHASE (WYE) = 10.571 Ω